- DFT 17
- Quantum Mechanics 10
- Inorganic Chemistry 10
- VASP 4
- Quantum Chemistry 3
- Band gap 3
- Basis set 2
- Solid state phyics 2
- electrocatalysis 2
- CO2 2
- Implicit solvation 2
- Python 2
- Anaconda 2
- CO2RR 2
- Linux 2
- blog 1
- TMP Chem 1
- optimizer 1
- ionic minimization 1
- equation 1
- HTML 1
- Mathpix 1
- pandoc 1
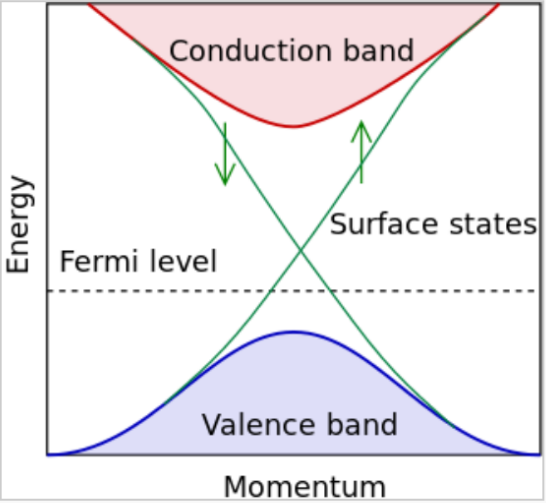
- Topological Insulators 1
- AGNR 1
- Quantum mechanics 1
- Quantum chemistry 1
- Surface chemistry 1
- Platinum 1
- Chemistry 1
- Periodic Table 1
- smearing 1
- Wavefunction 1
- Spin 1
- Environment 1
- Electrochemistry 1
- Linear Algebra 1
- Quantum Numbers 1
- electron configuration 1
- shielding 1
- Electron configuration 1
- Lewis electron-dot diagram 1
- octet rule 1
- Resonance 1
- Formal charge 1
- Expanded shell 1
- VSEPR 1
- Lone pair 1
- Steric number 1
- Electronegativity 1
- atomic size 1
- molecular geometry 1
- Dipole moment 1
- London dispersion force 1
- Hydrogen bond 1
- Symmetry element 1
- Symmetry operations 1
- Symmetry 1
- Point group 1
- Matrices 1
- optical activity 1
- IR activity 1
- Raman activity 1
- Molecular orbitals 1
- Bond order 1
- Oribtal mixing 1
- Magnetism 1
- Photoelectron spectroscopy 1
- Planewave 1
- k-points 1
- Equipment 1
- observable 1
- Ag(110) 1
- Continuum transport model 1
- Microkinetics 1
- Parallel computing 1
- JDFTx 1
- parallelization 1
- vibration 1
- Jmol 1
- Crystal field theory 1
- Ligand field theory 1
- Angular overlap method 1
- Bash 1
- Vibrational frequency 1
- Entropy 1
- Superconductivity 1
- Wannier 1
- Fourier Transformation 1
- Oxidation states 1
- virtual environment 1
- Assimulo 1
- Sundials 1
- CRYSTAL 1
- Global warming 1
- OVITO 1
- color coding 1
- air economy 1
- CO2 capture 1
- Water capture 1
- photocatalysis 1
- water splitting 1
- photovoltaics 1
- COOP 1
- COHP 1
- lobster 1
- Molecular dynamics 1
- Langevin dynamics 1
- Photoexcitation 1
- Mathematics 1
- ODE 1
- magnetism 1
- Collinear 1
- Noncollinear 1
- Dispersion 1
- HF 1
- Ab-initio 1
- Organic 1
- GSL 1
- MKL 1
- BLAS 1
- CBLAS 1
- LAPACK 1
- ScaLAPACK 1
DFT
Partial occupancy
The tetrahedron method with Blöchl corrections (ISMEAR=-5) gives a good account of the electronic density of states (DOS). The only drawback is that the method is not variational with respect to the partial occupancies. Therefore the calculated forces and the stress tensor can be wrong by up to 5 to 10% for metals. Only for semiconductors and insulators, the forces are correct because the partial occupancies do not vary and are either zero or one.
Counter charge
Electrode-Electrolyte Interface
RHF vs ROHF vs UHF
https://www.tau.ac.il/~ephraim/RHF.pdf
https://adreasnow.com/Undergrad/Notes/Sem%205.%20Comp%20Chemistry/05.%20Ab%20Initio/
CRYSTAL
linearly dependent basis set
EIGS (block 3): print out the eigenvalues of the overlap matrix (S)
This is a test run
1D DFT practice
1D DFT code
How to control a potential?
The electronic structure calculation spontaneously separates an electron from the extra hydrogen in the water layer to form a double layer capacitor.
Computational Electrochemistry
Temperature Smearing
Basis Set
Basis set
Basis Set Issues
Linear dependence
[1]
큰 basis set, 특히 diffuse function (or those with several closely spaced sets of off-centered functions)을 갖는 basis set으로 계산을 수행할 경우 linear dependency에 의한 numerical instabilities를 겪게 된다. 이러한 문제는 periodic systems나 large set of bonding functions를 사용하는 경우에 발생한다.
HF level과 correlated calculation에서의 문제의 성격이 약간 다른데, HF equations에서는 construction of an orthgonalizing transformation matrix S-1/2 (S: overlap matrix) 할 때 발생한다. near linear dependence basis set의 경우 S matrix의 eigenvalues가 너무 작아서 S-1/2을 구성할 때 nearly zero로 나눠야 하기 때문에 singularity가 발생하게 되고 따라서 precision에 영향을 미치게 된다. correlated calculation에서는 near linear dependence가 있으면 매우 큰 molecular orbital (MO) coefficients for virtual orbitals를 야기한다. 예를 들면, MO coefficient가 1000이면, 그러한 4 개의 coefficient들의 곱은 1012이 된다. two-electron integral의 정확도는 기껏해야 10-14 정도이기 때문에, the transformed integral은 매우 큰 numerical error를 가지게 된다.
이 문제의 심각성을 평가하는 방법으로는 overlap matrix S의 가장 작은 eigen value의 값을 측정하는 방법이 있다. 더 작은 eigen value를 가질수록 더 큰 linear dependence를 가진다. eigen value가 10-8 이하일 경우 심각한 numerical instability를 야기하게 되는데, 경우에 따라 10-7, 10-6 인 경우도 신뢰할 수 없는 결과를 만들기도 한다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위한 방법으로는 단순히 한 개 이상의 the most diffuse basis function을 생략하거나, 작은 eigen value를 야기하는 basis function의 linear combination을 생략하는 방법이 있다.
Gaussian 같은 프로그램들은 이것을 자동으로 해 주기도 한다. CRYSTAL code의 경우 [3]을 참고하자.
Interstitial Electron Model (IEM)
Band gap
Band gap
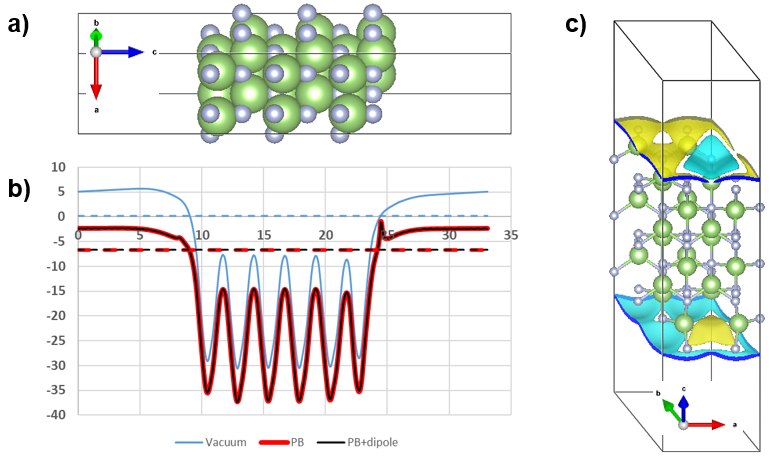
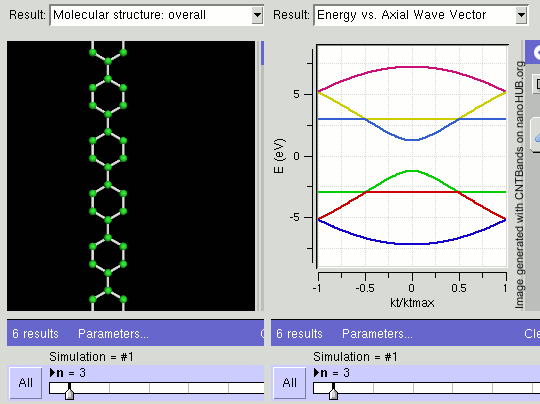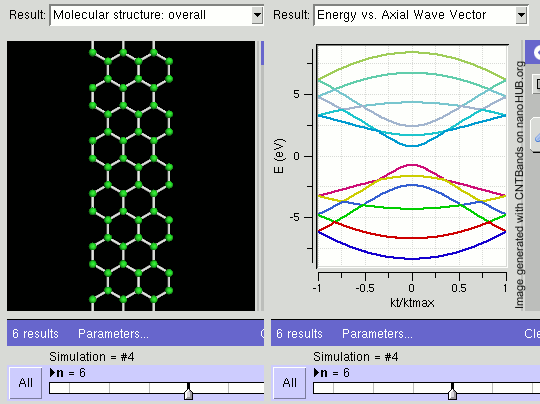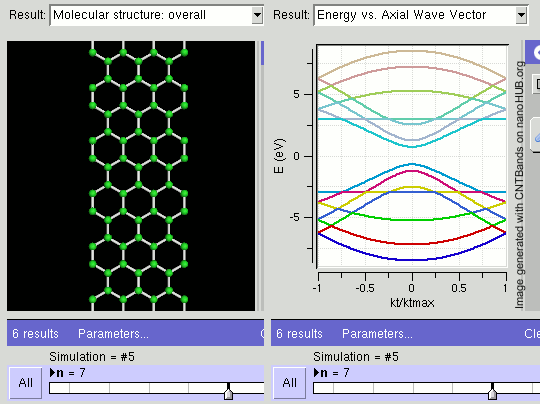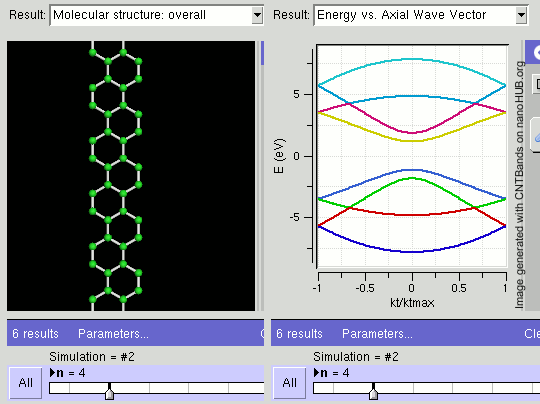
Armchair Graphene Nanoribbons (AGNR)
Topological Insulators
Grand canonical potential kinetics
Canonical
Optimizer
Force-based optimizer
quasi-Newton algorithm (RMM-DIIS) : IBRION = 1
POTIM : the step size in the steepest descent step
NFREE : s how many ionic steps are stored in the iteration history
Quantum Mechanics
RHF vs ROHF vs UHF
https://www.tau.ac.il/~ephraim/RHF.pdf
https://adreasnow.com/Undergrad/Notes/Sem%205.%20Comp%20Chemistry/05.%20Ab%20Initio/
Spin state
Wavefunction
Kronig-Penney Model
Band gap
Band gap
Armchair Graphene Nanoribbons (AGNR)
Topological Insulators
Grand canonical potential kinetics
Canonical
Antisymmetry and electron spin

7.11 Electron spin
7.11 Electron spin
Inorganic Chemistry
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Applications of Symmetry
Optical activity
Chirality
Mirror image에 중첩되지 않는 분자들을 chiral 또는 dissymmetric 하다고 한다. (dissymmetric 하다는 말이 곧 symmetry가 없다는 말은 아니다.) CBrClFI와 같은 분자처럼 E를 제외한 다른 symmetry operation이 없거나, only proper roation axis만 있을 때 그 분자를 chiral 하다고 말한다. 이러한 chiral 분자들은 빛을 편향시키는 성질이 있어 optical activity 가 있다. 빛을 시계방향으로 편향시키면 dextrorotatory, 반시계방향으로 편향시키면 levorotatory라고 한다.
Point Group
Point Groups
한 분자의 여러 symmetry operations을 하나의 set로 모아놓은 것 을 그 분자의 point group이라고 한다.
Point group을 결정하는 것은 아래의 diagram을 따라가기만 하면 된다. 다만 첫번째 step인 분자가 low (or high) symmetry를 가지고 있느냐만 집고 넘어가보자.
low symmetry는 symmetry가 없거나(E), 하나의 mirror plane (Cs)만 있거나, 하나의 inversion center (Ci) 만 있을 경우에 해당된다.
high symmetry는 여러가지가 있는데,
C∞υ: linear하고, inversion center가 없는 경우, HCl
D∞h: linear하고 perpendicular C2 axis, perpendicular mirror plane, inversion center가 존재하는 경우, CO2
Td: Tetrahedral, CH4
Oh: Ohtahedral, SF6
Ih: Icosahedral, B12H122-
Symmetry Elements and Operations
Symmetry
분자의 symmetry를 분석함으로써 optical activity 를 예측할 수 있고, infrared-active stretching vibration 의 수와 type을 결정할 수 있으며, 본딩에 사용된 orbital의 type 을 기술하기도 하고, electronic spectra 를 해석할 수 있다.
Polar Molecules
Dipole moment (μ)
서로 다른 두 electronegativity를 가진 원자가 결합하면 polar bond를 형성한다.
실험적으로는 간접적인 방법으로 dielectric constant를 측정하여 이를 계산한다.
polar molecule의 경우 electric field를 상쇄시키는 방향으로 정렬되기 때문에 큰 dielectric constant를 가진다.
여러 온도에서의 측정을 통하여 dipole moment (μ)를 계산하게 되는데, μ = Qr로 정의된다.
복잡한 분자에서는 단순히 각각의 bond dipole moment의 합으로 net molecular dipole moment를 계산하긴 어렵다.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity는 단순히 formar charge argument를 가이드하는 것 뿐만 아니라, cetral atom 주위의 outer atom들의 arrangement를 이해하는데 중요한 역할을 한다.
Electronegativity는 사실 bond energy를 기술하기 위해 도입되었다. (Linus Pauling, 1930)
Polar bond energy는 각각의 homonuclear species의 bond energy의 평균보다 크다. (HCl = 428 kJ/mol > 336 kJ/mol = { 432 (H2) + 240 (Cl2) }
이러한 bond energy data를 이용하여 Pauling이 electronegativity를 계산했는데, 최근에는 molecular or atomic property를 이용한 electronegativity scale이 몇 가지 있다. 다만, ionization potential을 이용하든 atomic property를 이용하든 간에 electronegativity는 molecule의 structure에 의존하기 때문에 실제 값은 달라질 수 있다.
Noble gas를 제외하면, F가 가장 큰 electronegativity을 가지고, 주기율표에서 왼쪽 아래로 내려갈 수록 그 값은 작아진다.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) 는 electron pair 사이의 electrostatic repulsion 을 기반으로 분자의 모양을 예측한다.
기본적으로 lone pair든, single bond든, multiple bond든 분자의 모양을 예측할 때는 비슷한 기여를 한다고 생각한다. 다만 그 정도의 차이가 있을 뿐.
이를 통해서 왜 암모니아의 H-N-H angle이 물분자의 H-O-H angle보다 큰지 이해할 수 있다.
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
Electron configurations
‘Abnormal’ electron configuration
Quantum Numbers
Principal quantum number (n)
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …
Determines the major part of the energy
VASP
Electron-phonon coupling
Visualization of vibration mode
VASP의 vibration 모드를 Jmol을 이용해서 visualization 해보자.
OUTCAR에 이미 cartesian coordinate으로 변환된 Eigenvector와 해당 eigenvalue가 완성되어 있으므로, 앞에 원소만 표기해줘서 xyz 파일로 만들면 Jmol에서 시각화 할 수 있다.
DFT parallelization
Optimizer
Force-based optimizer
quasi-Newton algorithm (RMM-DIIS) : IBRION = 1
POTIM : the step size in the steepest descent step
NFREE : s how many ionic steps are stored in the iteration history
Quantum Chemistry
How to control a potential?
The electronic structure calculation spontaneously separates an electron from the extra hydrogen in the water layer to form a double layer capacitor.
Spin state
7.11 Electron spin
7.11 Electron spin
Band gap
Back to Top ↑Basis set
Basis Set
Basis set
Basis Set Issues
Linear dependence
[1]
큰 basis set, 특히 diffuse function (or those with several closely spaced sets of off-centered functions)을 갖는 basis set으로 계산을 수행할 경우 linear dependency에 의한 numerical instabilities를 겪게 된다. 이러한 문제는 periodic systems나 large set of bonding functions를 사용하는 경우에 발생한다.
HF level과 correlated calculation에서의 문제의 성격이 약간 다른데, HF equations에서는 construction of an orthgonalizing transformation matrix S-1/2 (S: overlap matrix) 할 때 발생한다. near linear dependence basis set의 경우 S matrix의 eigenvalues가 너무 작아서 S-1/2을 구성할 때 nearly zero로 나눠야 하기 때문에 singularity가 발생하게 되고 따라서 precision에 영향을 미치게 된다. correlated calculation에서는 near linear dependence가 있으면 매우 큰 molecular orbital (MO) coefficients for virtual orbitals를 야기한다. 예를 들면, MO coefficient가 1000이면, 그러한 4 개의 coefficient들의 곱은 1012이 된다. two-electron integral의 정확도는 기껏해야 10-14 정도이기 때문에, the transformed integral은 매우 큰 numerical error를 가지게 된다.
이 문제의 심각성을 평가하는 방법으로는 overlap matrix S의 가장 작은 eigen value의 값을 측정하는 방법이 있다. 더 작은 eigen value를 가질수록 더 큰 linear dependence를 가진다. eigen value가 10-8 이하일 경우 심각한 numerical instability를 야기하게 되는데, 경우에 따라 10-7, 10-6 인 경우도 신뢰할 수 없는 결과를 만들기도 한다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위한 방법으로는 단순히 한 개 이상의 the most diffuse basis function을 생략하거나, 작은 eigen value를 야기하는 basis function의 linear combination을 생략하는 방법이 있다.
Gaussian 같은 프로그램들은 이것을 자동으로 해 주기도 한다. CRYSTAL code의 경우 [3]을 참고하자.
Solid state phyics
Back to Top ↑electrocatalysis
Photoelectrocatalytic Water Splitting
광합성은 태양에너지와 물, 이산화탄소를 이용하여 바이오매스와 산소를 얻는 과정이다. 대부분 사람들이 잊어버리는 것중 하나는 이 광합성은 사실 2-step process라는 것. 식물은 빛을 이용하여 물을 분해하여 산소와 수소(NADPH)를 생성하지만, 수소와 CO2를 이용하여 바이오매스를 생산하는 과정은 빛을 필요로 하지 않는다.
물분해는 열역학적으로 uphill. 하지만 우리가 이미 수소를 가지고 있다면, 이산화탄소를 환원해서 얻는 거의 모든 종류의 carbon product생산하는 것은 열역학적으로 thermoneutral이거나 downhill.
광합성은 사실 에너지를 저장하기 위한 최적의 시스템은 아니다. 왜냐하면 생물은 에너지를 저장하기보다 에너지를 쓰는데 더 집중하기 때문. 실제 광합성을 통한 에너지 저장 효율은 10.5 % 정도로, 일반적인 실리콘태양전지(> 25 %)의 효율보다도 낮다.
Computational Electrochemistry
CO2
Global Warming
CO2 vs temperature
Why reducing our carbon emissions matters (a little story about climate change)
Carbon dioxide over 800,000 years
CO2
The Carbon Cycle
Daily CO2 concentration
Carbon dioxide peaks near 420 parts per million
Changes in the World’s Top 10 Emitters
Global Carbon Budget 2019, [Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 2019, 11, 1783–1838] (https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-11-1783-2019)
Climate Reanalyzer
Global Temperature
CO2 as a greenhouse gas
Implicit solvation
Implicit solvation model
Implicit solvation을 이용하면 효율적이로 solvent 거동에 대한 적당한 묘사가 가능하지만 solute 주변에 있는 solvation density에 대한 local fluctuations에 대한 고려는 하지 못한다. 이러한 density fluctuation은 solute 주변의 solvent ordering에 의해 발생하는데, 특히 solvent가 water일때 특히 중요하다.
Poisson-Boltzmann equation
Python
Anaconda
가상환경 사용하기
https://nhlmary3.tistory.com/entry/Conda-Environment
1D DFT practice
1D DFT code
Anaconda
Anaconda Virtual Environment
miniconda 가 Anaconda보다 훨씬 가볍기 때문에, Miniconda를 설치할 것을 추천한다.
또한 miniconda 설치시 설치 경로에 띄어쓰기가 들어가지 않도록 주의해야 한다. 몇몇 패키지의(예: assimulo) 설치에 문제가 생길 수 있기 때문.
“사용자”가 아닌 “공용”으로 쓰도록 miniconda를 설치하고 필요한 가상환경이나 패키지가 있을 경우에는 prompt를 사용자 권한으로 실행시킨 후 각각 설치하는 것이 깔끔하다. 이렇게 하면 miniconda는 C:\ProgramData 에 설치되게 된다.
Anaconda
가상환경 사용하기
https://nhlmary3.tistory.com/entry/Conda-Environment
CO2RR
CO2RR
Technoeconomic analysis
What would it take for renewably powered electrosynthesis to displace petrochemical processes?
- Among carbon-based commodity chemicals, ethylene (C2H4) has the largest global market size at $230 B and the highest impact on emission reduction, potentially reducing 862 Mt CO2 per year. (Ethanol: $75 B, 546 Mt)
- Catalysts should last for thousands of hours of continuous operation.
- Renewable electricity cost should fall below 4 cents/kWh.
- Energy conversion efficiency should reach to at least 60 %.
Continuum Transport Model
Linux
Bash
shell is not a programing language, but just collection of different programs. Normally they works together very well.
Slurm
blog
Blogging List
Blogging List
spintronics
- https://depletionregion.tistory.com/notice/149
TMP Chem
7.11 Electron spin
7.11 Electron spin
optimizer
Optimizer
Force-based optimizer
quasi-Newton algorithm (RMM-DIIS) : IBRION = 1
POTIM : the step size in the steepest descent step
NFREE : s how many ionic steps are stored in the iteration history
ionic minimization
Optimizer
Force-based optimizer
quasi-Newton algorithm (RMM-DIIS) : IBRION = 1
POTIM : the step size in the steepest descent step
NFREE : s how many ionic steps are stored in the iteration history
equation
Expression of an equation in HTML
Expression of an equation in HTML
HTML
Expression of an equation in HTML
Expression of an equation in HTML
Mathpix
Expression of an equation in HTML
Expression of an equation in HTML
pandoc
Expression of an equation in HTML
Expression of an equation in HTML
Topological Insulators
Back to Top ↑AGNR
Back to Top ↑Quantum mechanics
Back to Top ↑Quantum chemistry
Back to Top ↑Surface chemistry
Back to Top ↑Platinum
Back to Top ↑Chemistry
Periodic table
reference
PubChem
Periodic Table
Periodic table

reference
PubChem
smearing
Back to Top ↑Wavefunction
Back to Top ↑Spin
Back to Top ↑Environment
Back to Top ↑Electrochemistry
How to control a potential?
The electronic structure calculation spontaneously separates an electron from the extra hydrogen in the water layer to form a double layer capacitor.
Linear Algebra
Back to Top ↑Quantum Numbers
Quantum Numbers
Principal quantum number (n)
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …
Determines the major part of the energy
electron configuration
Electron configurations
‘Abnormal’ electron configuration
shielding
Electron configurations
‘Abnormal’ electron configuration
Electron configuration
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
Lewis electron-dot diagram
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
octet rule
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
Resonance
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
Formal charge
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
Expanded shell
Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
Lewis electron-dot diagram
noble gas 처럼 s2p6 configuration을 만족할 경우, 즉 valence electron이 8개 일 경우 특별히 안정하다고 가정. (Octet rule)
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) 는 electron pair 사이의 electrostatic repulsion 을 기반으로 분자의 모양을 예측한다.
기본적으로 lone pair든, single bond든, multiple bond든 분자의 모양을 예측할 때는 비슷한 기여를 한다고 생각한다. 다만 그 정도의 차이가 있을 뿐.
이를 통해서 왜 암모니아의 H-N-H angle이 물분자의 H-O-H angle보다 큰지 이해할 수 있다.
Lone pair
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) 는 electron pair 사이의 electrostatic repulsion 을 기반으로 분자의 모양을 예측한다.
기본적으로 lone pair든, single bond든, multiple bond든 분자의 모양을 예측할 때는 비슷한 기여를 한다고 생각한다. 다만 그 정도의 차이가 있을 뿐.
이를 통해서 왜 암모니아의 H-N-H angle이 물분자의 H-O-H angle보다 큰지 이해할 수 있다.
Steric number
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) 는 electron pair 사이의 electrostatic repulsion 을 기반으로 분자의 모양을 예측한다.
기본적으로 lone pair든, single bond든, multiple bond든 분자의 모양을 예측할 때는 비슷한 기여를 한다고 생각한다. 다만 그 정도의 차이가 있을 뿐.
이를 통해서 왜 암모니아의 H-N-H angle이 물분자의 H-O-H angle보다 큰지 이해할 수 있다.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity는 단순히 formar charge argument를 가이드하는 것 뿐만 아니라, cetral atom 주위의 outer atom들의 arrangement를 이해하는데 중요한 역할을 한다.
Electronegativity는 사실 bond energy를 기술하기 위해 도입되었다. (Linus Pauling, 1930)
Polar bond energy는 각각의 homonuclear species의 bond energy의 평균보다 크다. (HCl = 428 kJ/mol > 336 kJ/mol = { 432 (H2) + 240 (Cl2) }
이러한 bond energy data를 이용하여 Pauling이 electronegativity를 계산했는데, 최근에는 molecular or atomic property를 이용한 electronegativity scale이 몇 가지 있다. 다만, ionization potential을 이용하든 atomic property를 이용하든 간에 electronegativity는 molecule의 structure에 의존하기 때문에 실제 값은 달라질 수 있다.
Noble gas를 제외하면, F가 가장 큰 electronegativity을 가지고, 주기율표에서 왼쪽 아래로 내려갈 수록 그 값은 작아진다.
atomic size
Electronegativity
Electronegativity는 단순히 formar charge argument를 가이드하는 것 뿐만 아니라, cetral atom 주위의 outer atom들의 arrangement를 이해하는데 중요한 역할을 한다.
Electronegativity는 사실 bond energy를 기술하기 위해 도입되었다. (Linus Pauling, 1930)
Polar bond energy는 각각의 homonuclear species의 bond energy의 평균보다 크다. (HCl = 428 kJ/mol > 336 kJ/mol = { 432 (H2) + 240 (Cl2) }
이러한 bond energy data를 이용하여 Pauling이 electronegativity를 계산했는데, 최근에는 molecular or atomic property를 이용한 electronegativity scale이 몇 가지 있다. 다만, ionization potential을 이용하든 atomic property를 이용하든 간에 electronegativity는 molecule의 structure에 의존하기 때문에 실제 값은 달라질 수 있다.
Noble gas를 제외하면, F가 가장 큰 electronegativity을 가지고, 주기율표에서 왼쪽 아래로 내려갈 수록 그 값은 작아진다.
molecular geometry
Electronegativity
Electronegativity는 단순히 formar charge argument를 가이드하는 것 뿐만 아니라, cetral atom 주위의 outer atom들의 arrangement를 이해하는데 중요한 역할을 한다.
Electronegativity는 사실 bond energy를 기술하기 위해 도입되었다. (Linus Pauling, 1930)
Polar bond energy는 각각의 homonuclear species의 bond energy의 평균보다 크다. (HCl = 428 kJ/mol > 336 kJ/mol = { 432 (H2) + 240 (Cl2) }
이러한 bond energy data를 이용하여 Pauling이 electronegativity를 계산했는데, 최근에는 molecular or atomic property를 이용한 electronegativity scale이 몇 가지 있다. 다만, ionization potential을 이용하든 atomic property를 이용하든 간에 electronegativity는 molecule의 structure에 의존하기 때문에 실제 값은 달라질 수 있다.
Noble gas를 제외하면, F가 가장 큰 electronegativity을 가지고, 주기율표에서 왼쪽 아래로 내려갈 수록 그 값은 작아진다.
Dipole moment
Polar Molecules
Dipole moment (μ)
서로 다른 두 electronegativity를 가진 원자가 결합하면 polar bond를 형성한다.
실험적으로는 간접적인 방법으로 dielectric constant를 측정하여 이를 계산한다.
polar molecule의 경우 electric field를 상쇄시키는 방향으로 정렬되기 때문에 큰 dielectric constant를 가진다.
여러 온도에서의 측정을 통하여 dipole moment (μ)를 계산하게 되는데, μ = Qr로 정의된다.
복잡한 분자에서는 단순히 각각의 bond dipole moment의 합으로 net molecular dipole moment를 계산하긴 어렵다.
London dispersion force
Polar Molecules
Dipole moment (μ)
서로 다른 두 electronegativity를 가진 원자가 결합하면 polar bond를 형성한다.
실험적으로는 간접적인 방법으로 dielectric constant를 측정하여 이를 계산한다.
polar molecule의 경우 electric field를 상쇄시키는 방향으로 정렬되기 때문에 큰 dielectric constant를 가진다.
여러 온도에서의 측정을 통하여 dipole moment (μ)를 계산하게 되는데, μ = Qr로 정의된다.
복잡한 분자에서는 단순히 각각의 bond dipole moment의 합으로 net molecular dipole moment를 계산하긴 어렵다.
Hydrogen bond
Polar Molecules
Dipole moment (μ)
서로 다른 두 electronegativity를 가진 원자가 결합하면 polar bond를 형성한다.
실험적으로는 간접적인 방법으로 dielectric constant를 측정하여 이를 계산한다.
polar molecule의 경우 electric field를 상쇄시키는 방향으로 정렬되기 때문에 큰 dielectric constant를 가진다.
여러 온도에서의 측정을 통하여 dipole moment (μ)를 계산하게 되는데, μ = Qr로 정의된다.
복잡한 분자에서는 단순히 각각의 bond dipole moment의 합으로 net molecular dipole moment를 계산하긴 어렵다.
Symmetry element
Symmetry Elements and Operations
Symmetry
분자의 symmetry를 분석함으로써 optical activity 를 예측할 수 있고, infrared-active stretching vibration 의 수와 type을 결정할 수 있으며, 본딩에 사용된 orbital의 type 을 기술하기도 하고, electronic spectra 를 해석할 수 있다.
Symmetry operations
Symmetry Elements and Operations
Symmetry
분자의 symmetry를 분석함으로써 optical activity 를 예측할 수 있고, infrared-active stretching vibration 의 수와 type을 결정할 수 있으며, 본딩에 사용된 orbital의 type 을 기술하기도 하고, electronic spectra 를 해석할 수 있다.
Symmetry
Point Group
Point Groups
한 분자의 여러 symmetry operations을 하나의 set로 모아놓은 것 을 그 분자의 point group이라고 한다.
Point group을 결정하는 것은 아래의 diagram을 따라가기만 하면 된다. 다만 첫번째 step인 분자가 low (or high) symmetry를 가지고 있느냐만 집고 넘어가보자.
low symmetry는 symmetry가 없거나(E), 하나의 mirror plane (Cs)만 있거나, 하나의 inversion center (Ci) 만 있을 경우에 해당된다.
high symmetry는 여러가지가 있는데,
C∞υ: linear하고, inversion center가 없는 경우, HCl
D∞h: linear하고 perpendicular C2 axis, perpendicular mirror plane, inversion center가 존재하는 경우, CO2
Td: Tetrahedral, CH4
Oh: Ohtahedral, SF6
Ih: Icosahedral, B12H122-
Point group
Point Group
Point Groups
한 분자의 여러 symmetry operations을 하나의 set로 모아놓은 것 을 그 분자의 point group이라고 한다.
Point group을 결정하는 것은 아래의 diagram을 따라가기만 하면 된다. 다만 첫번째 step인 분자가 low (or high) symmetry를 가지고 있느냐만 집고 넘어가보자.
low symmetry는 symmetry가 없거나(E), 하나의 mirror plane (Cs)만 있거나, 하나의 inversion center (Ci) 만 있을 경우에 해당된다.
high symmetry는 여러가지가 있는데,
C∞υ: linear하고, inversion center가 없는 경우, HCl
D∞h: linear하고 perpendicular C2 axis, perpendicular mirror plane, inversion center가 존재하는 경우, CO2
Td: Tetrahedral, CH4
Oh: Ohtahedral, SF6
Ih: Icosahedral, B12H122-
Matrices
Point Group
Point Groups
한 분자의 여러 symmetry operations을 하나의 set로 모아놓은 것 을 그 분자의 point group이라고 한다.
Point group을 결정하는 것은 아래의 diagram을 따라가기만 하면 된다. 다만 첫번째 step인 분자가 low (or high) symmetry를 가지고 있느냐만 집고 넘어가보자.
low symmetry는 symmetry가 없거나(E), 하나의 mirror plane (Cs)만 있거나, 하나의 inversion center (Ci) 만 있을 경우에 해당된다.
high symmetry는 여러가지가 있는데,
C∞υ: linear하고, inversion center가 없는 경우, HCl
D∞h: linear하고 perpendicular C2 axis, perpendicular mirror plane, inversion center가 존재하는 경우, CO2
Td: Tetrahedral, CH4
Oh: Ohtahedral, SF6
Ih: Icosahedral, B12H122-
optical activity
Applications of Symmetry
Optical activity
Chirality
Mirror image에 중첩되지 않는 분자들을 chiral 또는 dissymmetric 하다고 한다. (dissymmetric 하다는 말이 곧 symmetry가 없다는 말은 아니다.) CBrClFI와 같은 분자처럼 E를 제외한 다른 symmetry operation이 없거나, only proper roation axis만 있을 때 그 분자를 chiral 하다고 말한다. 이러한 chiral 분자들은 빛을 편향시키는 성질이 있어 optical activity 가 있다. 빛을 시계방향으로 편향시키면 dextrorotatory, 반시계방향으로 편향시키면 levorotatory라고 한다.
IR activity
Applications of Symmetry
Optical activity
Chirality
Mirror image에 중첩되지 않는 분자들을 chiral 또는 dissymmetric 하다고 한다. (dissymmetric 하다는 말이 곧 symmetry가 없다는 말은 아니다.) CBrClFI와 같은 분자처럼 E를 제외한 다른 symmetry operation이 없거나, only proper roation axis만 있을 때 그 분자를 chiral 하다고 말한다. 이러한 chiral 분자들은 빛을 편향시키는 성질이 있어 optical activity 가 있다. 빛을 시계방향으로 편향시키면 dextrorotatory, 반시계방향으로 편향시키면 levorotatory라고 한다.
Raman activity
Applications of Symmetry
Optical activity
Chirality
Mirror image에 중첩되지 않는 분자들을 chiral 또는 dissymmetric 하다고 한다. (dissymmetric 하다는 말이 곧 symmetry가 없다는 말은 아니다.) CBrClFI와 같은 분자처럼 E를 제외한 다른 symmetry operation이 없거나, only proper roation axis만 있을 때 그 분자를 chiral 하다고 말한다. 이러한 chiral 분자들은 빛을 편향시키는 성질이 있어 optical activity 가 있다. 빛을 시계방향으로 편향시키면 dextrorotatory, 반시계방향으로 편향시키면 levorotatory라고 한다.
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Bond order
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Oribtal mixing
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Magnetism
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Photoelectron spectroscopy
Molecular orbitals
Molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals
분자의 Schrödinger equation을 풀면 대략적인 solution으로서 linear combination of the atomic orbitals (LCAO)를 구성할 수 있는데, LCAO란 원자의 wavefunction의 합 또는 차이다. H2를 예로 들면,
Planewave
Back to Top ↑k-points
Back to Top ↑Equipment
equipment vs observable
XAS
XAS vs observable
oxidation state of an element
interpretation
Nong, et al., Nature 2020, 587, 408, 10.1038/s41586-020-2908-2
- operando XAS: hole concentration by quantifying the number of empty 5d states of Ir from Ir L2,3 edge
- O 2p hole character, μ2-O (529 eV) and μ1-O oxyl (528.3 eV) from O K-edge XAS
observable
equipment vs observable
XAS
XAS vs observable
oxidation state of an element
interpretation
Nong, et al., Nature 2020, 587, 408, 10.1038/s41586-020-2908-2
- operando XAS: hole concentration by quantifying the number of empty 5d states of Ir from Ir L2,3 edge
- O 2p hole character, μ2-O (529 eV) and μ1-O oxyl (528.3 eV) from O K-edge XAS
Ag(110)
Back to Top ↑Continuum transport model
Back to Top ↑Microkinetics
Back to Top ↑Parallel computing
Back to Top ↑JDFTx
Back to Top ↑parallelization
Back to Top ↑vibration
Visualization of vibration mode
VASP의 vibration 모드를 Jmol을 이용해서 visualization 해보자.
OUTCAR에 이미 cartesian coordinate으로 변환된 Eigenvector와 해당 eigenvalue가 완성되어 있으므로, 앞에 원소만 표기해줘서 xyz 파일로 만들면 Jmol에서 시각화 할 수 있다.
Jmol
Visualization of vibration mode
VASP의 vibration 모드를 Jmol을 이용해서 visualization 해보자.
OUTCAR에 이미 cartesian coordinate으로 변환된 Eigenvector와 해당 eigenvalue가 완성되어 있으므로, 앞에 원소만 표기해줘서 xyz 파일로 만들면 Jmol에서 시각화 할 수 있다.
Crystal field theory
Coordination Chemistry
Crystal field theory
Crystal field theory는 기본적으로 oxide ion과 다른 anion에 둘러싸인 metal ion의 전자구조를 설명하기 위해 개발된 이론이므로, bonding에 대한 기술을 하지 않는다.
Ligand의 electron pair에 의해 생긴 electrostatic field에 의해 d electron이 불안정해진다.
Octahedral field 에서는 dx2-y2과 dz2이 ligand를 향해 위치하므로, ligand 주변 을 향해있는 dxy, dxz, dyz orbital에 비해 더 에너지가 높아진다.
이러한 결과로 생긴 eg와 t2g orbital간의 에너지 차이는 Δo으로 표현한다. (여기서 o는 octahedral)
만약 모든 orbital에 동일한 영향을 미치는 spherical field가 있다고 가정하면 모든 d orbital의 에너지는 일정하게 올라간다. (Average energy)
Octahedral field에서는 두 개의 eg orbital은 average energy보다 +0.6Δo만큼 높고, 3개의 t2g orbital은 -0.4Δo 만큼 낮다. 따라서 이 오비탈에너지의 총합은 2×0.6 - 3×0.4 = 0
Ligand field theory
Coordination Chemistry
Crystal field theory
Crystal field theory는 기본적으로 oxide ion과 다른 anion에 둘러싸인 metal ion의 전자구조를 설명하기 위해 개발된 이론이므로, bonding에 대한 기술을 하지 않는다.
Ligand의 electron pair에 의해 생긴 electrostatic field에 의해 d electron이 불안정해진다.
Octahedral field 에서는 dx2-y2과 dz2이 ligand를 향해 위치하므로, ligand 주변 을 향해있는 dxy, dxz, dyz orbital에 비해 더 에너지가 높아진다.
이러한 결과로 생긴 eg와 t2g orbital간의 에너지 차이는 Δo으로 표현한다. (여기서 o는 octahedral)
만약 모든 orbital에 동일한 영향을 미치는 spherical field가 있다고 가정하면 모든 d orbital의 에너지는 일정하게 올라간다. (Average energy)
Octahedral field에서는 두 개의 eg orbital은 average energy보다 +0.6Δo만큼 높고, 3개의 t2g orbital은 -0.4Δo 만큼 낮다. 따라서 이 오비탈에너지의 총합은 2×0.6 - 3×0.4 = 0
Angular overlap method
Coordination Chemistry
Crystal field theory
Crystal field theory는 기본적으로 oxide ion과 다른 anion에 둘러싸인 metal ion의 전자구조를 설명하기 위해 개발된 이론이므로, bonding에 대한 기술을 하지 않는다.
Ligand의 electron pair에 의해 생긴 electrostatic field에 의해 d electron이 불안정해진다.
Octahedral field 에서는 dx2-y2과 dz2이 ligand를 향해 위치하므로, ligand 주변 을 향해있는 dxy, dxz, dyz orbital에 비해 더 에너지가 높아진다.
이러한 결과로 생긴 eg와 t2g orbital간의 에너지 차이는 Δo으로 표현한다. (여기서 o는 octahedral)
만약 모든 orbital에 동일한 영향을 미치는 spherical field가 있다고 가정하면 모든 d orbital의 에너지는 일정하게 올라간다. (Average energy)
Octahedral field에서는 두 개의 eg orbital은 average energy보다 +0.6Δo만큼 높고, 3개의 t2g orbital은 -0.4Δo 만큼 낮다. 따라서 이 오비탈에너지의 총합은 2×0.6 - 3×0.4 = 0
Bash
Bash
shell is not a programing language, but just collection of different programs. Normally they works together very well.
Vibrational frequency
vibrational contribution to free energy
the vibrational contribution to molar entropy
Entropy
vibrational contribution to free energy
the vibrational contribution to molar entropy
Superconductivity
Superconductivity
DFPT
Density Functional Perturbation Theory
Density Functional Perturbation Theory and Electron Phonon Coupling
For DFPT: VASP vs QE
abipy: output from Abinit.
python code for JDFTx calculations: Electron-phonon matrix elements
Wannier
MLWF
Maximally-localized Wannier functions (MLWF)
Fourier Transformation
Fourier Transformation
Desktop\Project\Mathematics\Descrete_Fourier_Transform_1.ipynb
Oxidation states
Oxidation states
Electron Counting in Solids: Oxidation States, Partial Charges, and Ionicity
Crystal 내의 electron은 multicentered wave functions (Bloch waves)에 의해 기술되므로 charge assigning은 어렵다.
다만 실험과 비교해 볼 수 있는 것으로는,
- Lattice energy
- Response to electromagnetic fields
- Core-level photoemission spectrscopy
- Electron spin resonance (ESR)
- nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
virtual environment
Anaconda Virtual Environment
miniconda 가 Anaconda보다 훨씬 가볍기 때문에, Miniconda를 설치할 것을 추천한다.
또한 miniconda 설치시 설치 경로에 띄어쓰기가 들어가지 않도록 주의해야 한다. 몇몇 패키지의(예: assimulo) 설치에 문제가 생길 수 있기 때문.
“사용자”가 아닌 “공용”으로 쓰도록 miniconda를 설치하고 필요한 가상환경이나 패키지가 있을 경우에는 prompt를 사용자 권한으로 실행시킨 후 각각 설치하는 것이 깔끔하다. 이렇게 하면 miniconda는 C:\ProgramData 에 설치되게 된다.
Assimulo
Assiumlo
Convergence
initial condition 이 convergence 및 결과에 매우 중요하다.
initial step size가 작을수록 초기 initial condition의 수렴에 유리하다. (imp_sim.inith = 1e-15)
convergence가 안 좋으면 기본적으로 code가 더 작은 step size로 계산을 진행하긴 한다. 그래도 max step size를 정하고 싶다면 maximal step-size를 이용하자.
결과값이 시간에 따라 잘 수렴하지 않으면, 시간에 따른 absolute error를 살펴보자.
Sundials
Assiumlo
Convergence
initial condition 이 convergence 및 결과에 매우 중요하다.
initial step size가 작을수록 초기 initial condition의 수렴에 유리하다. (imp_sim.inith = 1e-15)
convergence가 안 좋으면 기본적으로 code가 더 작은 step size로 계산을 진행하긴 한다. 그래도 max step size를 정하고 싶다면 maximal step-size를 이용하자.
결과값이 시간에 따라 잘 수렴하지 않으면, 시간에 따른 absolute error를 살펴보자.
CRYSTAL
CRYSTAL
linearly dependent basis set
EIGS (block 3): print out the eigenvalues of the overlap matrix (S)
This is a test run
Global warming
Global Warming
CO2 vs temperature
Why reducing our carbon emissions matters (a little story about climate change)
Carbon dioxide over 800,000 years
CO2
The Carbon Cycle
Daily CO2 concentration
Carbon dioxide peaks near 420 parts per million
Changes in the World’s Top 10 Emitters
Global Carbon Budget 2019, [Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 2019, 11, 1783–1838] (https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-11-1783-2019)
Climate Reanalyzer
Global Temperature
OVITO
OVITO
Color coding
OVITO Modifiers for Crystal Structures
OVITO에서 atomic properties or local geometry에 따라 color coding을 할 수 있다.
Add modification에서 원하는 analysis를 선택하고, Coloring - Color coding 을 클릭하면 된다.
color coding
OVITO
Color coding
OVITO Modifiers for Crystal Structures
OVITO에서 atomic properties or local geometry에 따라 color coding을 할 수 있다.
Add modification에서 원하는 analysis를 선택하고, Coloring - Color coding 을 클릭하면 된다.
air economy
Air Economy
- Currently 100,000 MOFs structures are known. The pore diameter range from 5 Å to 100 Å. Ultra-high surface area of up to 7,000 m2/g
- Captureing CO2 from air requires new materials capable of trapping carbon dioxide at 400-ppm levels.
- Zeolite (0.25 ~ 1.4 mmol/gCO2) requires very high regeneration T. Polymers (very low capacity), silica (0.1 ~ 1.8 mmol/gCO2), MOFs (0.1 to 4 mmol/gCO2) should be functionalized with primary amines to capture CO2. No MOF which can be recycled over a large number of cycles is yet to be reported.
- The current estimate of CO2 capture for direct air capture (DAC) systems spans a range of $100 ~ $1000/tCO2 while flue gas capture techniques can produce $70 ~ $100/tCO2
- Effective electro-catalysis coupled with high-efficiency stateof-the-art solar junctions can already deliver green hydrogen at ~30% solar-to-hydrogen efficiency.
- Water harvesting from air is already commercialized by Water Harvesting Inc. Their latest device employs only 200 g of MOF and can harvest water at the rate of 40 L per kilogram of MOF per day. The lifetime of MOF is 6 years. MOF can be treated with strong acid to dissociate the linker from the metal and resynthesized in water.
CO2 capture
Air Economy
- Currently 100,000 MOFs structures are known. The pore diameter range from 5 Å to 100 Å. Ultra-high surface area of up to 7,000 m2/g
- Captureing CO2 from air requires new materials capable of trapping carbon dioxide at 400-ppm levels.
- Zeolite (0.25 ~ 1.4 mmol/gCO2) requires very high regeneration T. Polymers (very low capacity), silica (0.1 ~ 1.8 mmol/gCO2), MOFs (0.1 to 4 mmol/gCO2) should be functionalized with primary amines to capture CO2. No MOF which can be recycled over a large number of cycles is yet to be reported.
- The current estimate of CO2 capture for direct air capture (DAC) systems spans a range of $100 ~ $1000/tCO2 while flue gas capture techniques can produce $70 ~ $100/tCO2
- Effective electro-catalysis coupled with high-efficiency stateof-the-art solar junctions can already deliver green hydrogen at ~30% solar-to-hydrogen efficiency.
- Water harvesting from air is already commercialized by Water Harvesting Inc. Their latest device employs only 200 g of MOF and can harvest water at the rate of 40 L per kilogram of MOF per day. The lifetime of MOF is 6 years. MOF can be treated with strong acid to dissociate the linker from the metal and resynthesized in water.
Water capture
Air Economy
- Currently 100,000 MOFs structures are known. The pore diameter range from 5 Å to 100 Å. Ultra-high surface area of up to 7,000 m2/g
- Captureing CO2 from air requires new materials capable of trapping carbon dioxide at 400-ppm levels.
- Zeolite (0.25 ~ 1.4 mmol/gCO2) requires very high regeneration T. Polymers (very low capacity), silica (0.1 ~ 1.8 mmol/gCO2), MOFs (0.1 to 4 mmol/gCO2) should be functionalized with primary amines to capture CO2. No MOF which can be recycled over a large number of cycles is yet to be reported.
- The current estimate of CO2 capture for direct air capture (DAC) systems spans a range of $100 ~ $1000/tCO2 while flue gas capture techniques can produce $70 ~ $100/tCO2
- Effective electro-catalysis coupled with high-efficiency stateof-the-art solar junctions can already deliver green hydrogen at ~30% solar-to-hydrogen efficiency.
- Water harvesting from air is already commercialized by Water Harvesting Inc. Their latest device employs only 200 g of MOF and can harvest water at the rate of 40 L per kilogram of MOF per day. The lifetime of MOF is 6 years. MOF can be treated with strong acid to dissociate the linker from the metal and resynthesized in water.
photocatalysis
Photoelectrocatalytic Water Splitting
광합성은 태양에너지와 물, 이산화탄소를 이용하여 바이오매스와 산소를 얻는 과정이다. 대부분 사람들이 잊어버리는 것중 하나는 이 광합성은 사실 2-step process라는 것. 식물은 빛을 이용하여 물을 분해하여 산소와 수소(NADPH)를 생성하지만, 수소와 CO2를 이용하여 바이오매스를 생산하는 과정은 빛을 필요로 하지 않는다.
물분해는 열역학적으로 uphill. 하지만 우리가 이미 수소를 가지고 있다면, 이산화탄소를 환원해서 얻는 거의 모든 종류의 carbon product생산하는 것은 열역학적으로 thermoneutral이거나 downhill.
광합성은 사실 에너지를 저장하기 위한 최적의 시스템은 아니다. 왜냐하면 생물은 에너지를 저장하기보다 에너지를 쓰는데 더 집중하기 때문. 실제 광합성을 통한 에너지 저장 효율은 10.5 % 정도로, 일반적인 실리콘태양전지(> 25 %)의 효율보다도 낮다.
water splitting
Photoelectrocatalytic Water Splitting
광합성은 태양에너지와 물, 이산화탄소를 이용하여 바이오매스와 산소를 얻는 과정이다. 대부분 사람들이 잊어버리는 것중 하나는 이 광합성은 사실 2-step process라는 것. 식물은 빛을 이용하여 물을 분해하여 산소와 수소(NADPH)를 생성하지만, 수소와 CO2를 이용하여 바이오매스를 생산하는 과정은 빛을 필요로 하지 않는다.
물분해는 열역학적으로 uphill. 하지만 우리가 이미 수소를 가지고 있다면, 이산화탄소를 환원해서 얻는 거의 모든 종류의 carbon product생산하는 것은 열역학적으로 thermoneutral이거나 downhill.
광합성은 사실 에너지를 저장하기 위한 최적의 시스템은 아니다. 왜냐하면 생물은 에너지를 저장하기보다 에너지를 쓰는데 더 집중하기 때문. 실제 광합성을 통한 에너지 저장 효율은 10.5 % 정도로, 일반적인 실리콘태양전지(> 25 %)의 효율보다도 낮다.
photovoltaics
Photovoltaics(PV)
Theoretical limit of solar cell under 1 sun irradiance (https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0022-3727/13/5/018/pdf)
- solar cell: 30%
- a tandem structure of two cell: 42%
- a tandem structure of three cell: 49%
COOP
COOP or COHP
고체의 bonding 특성을 알려줄 수 있는 indicator로 Crystal orbital overlap population (COOP)를 활용할 수 있다. 이것은 Overlap population-weighted density of state 로 Mulliken overlap poputation (2cicjSij) 을 활용한다. COOP는 DOS와 overlap population을 곱함으로써 구할 수 있는데, 이를 통해 bonding (in-phase, positive overlap population)과 antibonding (out-of-phase, negative overlap population) 또한 nonbinding interaction을 구분할 수 있다.
COHP 또한 하나의 a theoretical bond-detecting tool로서, band-structure energy를 orbital-pair interactions으로 partition 한다. 즉 근접한 원자 사이의 “bond-weighted” density-of-states를 계산한다. 핵심은 density matrix (where are the electrons?)와 Hamiltonian matrix (what do they do?) 를 곱하는 것이다. COHP는 tight-binding LMTO 와 SIESTA 에서 이용할 수 있지만, plane-wave methods에서는 wavefunctino의 delocalization nature 때문에 COHP analysis를 할 수 없다. 따라서 wavefunction을 local, auxiliary basis으로 projection하여 chemical information을 추출할 수 있다. COHP에서는 COOP에서와는 반대로 bonding character는 Hamiltonian off-site element (“hopping term”) 의 negative value에서 비롯되고, 반대로 antibonding interactions은 positive value에서 비롯된다. COHP diagram 은 bonding 과 antibonding contributions 을 band-structure energy에 대해 plot 한 것인데, DOS를 적분하면 시스템 내의 전체 전자수를 알 수 있는 것과 마찬가지로, COHP의 에너지를 적분하면 band 에너지의 특정 bond의 기여, bond strength [in eV]를 알 수 있다.
COHP
COOP or COHP
고체의 bonding 특성을 알려줄 수 있는 indicator로 Crystal orbital overlap population (COOP)를 활용할 수 있다. 이것은 Overlap population-weighted density of state 로 Mulliken overlap poputation (2cicjSij) 을 활용한다. COOP는 DOS와 overlap population을 곱함으로써 구할 수 있는데, 이를 통해 bonding (in-phase, positive overlap population)과 antibonding (out-of-phase, negative overlap population) 또한 nonbinding interaction을 구분할 수 있다.
COHP 또한 하나의 a theoretical bond-detecting tool로서, band-structure energy를 orbital-pair interactions으로 partition 한다. 즉 근접한 원자 사이의 “bond-weighted” density-of-states를 계산한다. 핵심은 density matrix (where are the electrons?)와 Hamiltonian matrix (what do they do?) 를 곱하는 것이다. COHP는 tight-binding LMTO 와 SIESTA 에서 이용할 수 있지만, plane-wave methods에서는 wavefunctino의 delocalization nature 때문에 COHP analysis를 할 수 없다. 따라서 wavefunction을 local, auxiliary basis으로 projection하여 chemical information을 추출할 수 있다. COHP에서는 COOP에서와는 반대로 bonding character는 Hamiltonian off-site element (“hopping term”) 의 negative value에서 비롯되고, 반대로 antibonding interactions은 positive value에서 비롯된다. COHP diagram 은 bonding 과 antibonding contributions 을 band-structure energy에 대해 plot 한 것인데, DOS를 적분하면 시스템 내의 전체 전자수를 알 수 있는 것과 마찬가지로, COHP의 에너지를 적분하면 band 에너지의 특정 bond의 기여, bond strength [in eV]를 알 수 있다.
lobster
COOP or COHP
고체의 bonding 특성을 알려줄 수 있는 indicator로 Crystal orbital overlap population (COOP)를 활용할 수 있다. 이것은 Overlap population-weighted density of state 로 Mulliken overlap poputation (2cicjSij) 을 활용한다. COOP는 DOS와 overlap population을 곱함으로써 구할 수 있는데, 이를 통해 bonding (in-phase, positive overlap population)과 antibonding (out-of-phase, negative overlap population) 또한 nonbinding interaction을 구분할 수 있다.
COHP 또한 하나의 a theoretical bond-detecting tool로서, band-structure energy를 orbital-pair interactions으로 partition 한다. 즉 근접한 원자 사이의 “bond-weighted” density-of-states를 계산한다. 핵심은 density matrix (where are the electrons?)와 Hamiltonian matrix (what do they do?) 를 곱하는 것이다. COHP는 tight-binding LMTO 와 SIESTA 에서 이용할 수 있지만, plane-wave methods에서는 wavefunctino의 delocalization nature 때문에 COHP analysis를 할 수 없다. 따라서 wavefunction을 local, auxiliary basis으로 projection하여 chemical information을 추출할 수 있다. COHP에서는 COOP에서와는 반대로 bonding character는 Hamiltonian off-site element (“hopping term”) 의 negative value에서 비롯되고, 반대로 antibonding interactions은 positive value에서 비롯된다. COHP diagram 은 bonding 과 antibonding contributions 을 band-structure energy에 대해 plot 한 것인데, DOS를 적분하면 시스템 내의 전체 전자수를 알 수 있는 것과 마찬가지로, COHP의 에너지를 적분하면 band 에너지의 특정 bond의 기여, bond strength [in eV]를 알 수 있다.
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Langevin dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Photoexcitation
Photoexcitation
photoexcitation induced time-dependent density functional theory molecular dynamics
Photoexcitation Induced Quantum Dynamics of Charge Density Wave and Emergence of a Collective Mode in 1T-TaS2
Supporting Information
Mathematics
Differential equations
Differential equation: an equation containing derivatives of an unknown function.
Ordinary differential equation (ODE): an equation that contains one or several derivatives of an unknown function.
Partial differential equations (PDEs): differential equations that involve partial derivaties of an unknown functino of two or more variables.
ODE
Differential equations
Differential equation: an equation containing derivatives of an unknown function.
Ordinary differential equation (ODE): an equation that contains one or several derivatives of an unknown function.
Partial differential equations (PDEs): differential equations that involve partial derivaties of an unknown functino of two or more variables.
magnetism
Collinear vs Noncollinear calculations
Chirality Waves in Two-Dimensional Magnets
Magnetism is a cooperative phenomenon where spins of magnetic ions spontaneously orient relative to each other below a certain ordering temperature. In principle, arbitrarily complex magnetic orderings are possible; however, the magnetic states encountered in nature tend to be simple, the most common being ferromagnetism (one atom in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(a)] and antiferromagnetism (two distinct atoms in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(b)]. More complex orders, such as noncollinear spirals [Fig. 1(d)] and various noncoplanar orders [e.g., Fig. 1(e)] are less common, typically arising from the interplay of magnetic exchange interactions, spin-orbit (SO) coupling, frustrated lattice structure, and magnetic field.
Collinear
Collinear vs Noncollinear calculations
Chirality Waves in Two-Dimensional Magnets
Magnetism is a cooperative phenomenon where spins of magnetic ions spontaneously orient relative to each other below a certain ordering temperature. In principle, arbitrarily complex magnetic orderings are possible; however, the magnetic states encountered in nature tend to be simple, the most common being ferromagnetism (one atom in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(a)] and antiferromagnetism (two distinct atoms in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(b)]. More complex orders, such as noncollinear spirals [Fig. 1(d)] and various noncoplanar orders [e.g., Fig. 1(e)] are less common, typically arising from the interplay of magnetic exchange interactions, spin-orbit (SO) coupling, frustrated lattice structure, and magnetic field.
Noncollinear
Collinear vs Noncollinear calculations
Chirality Waves in Two-Dimensional Magnets
Magnetism is a cooperative phenomenon where spins of magnetic ions spontaneously orient relative to each other below a certain ordering temperature. In principle, arbitrarily complex magnetic orderings are possible; however, the magnetic states encountered in nature tend to be simple, the most common being ferromagnetism (one atom in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(a)] and antiferromagnetism (two distinct atoms in magnetic unit cell, Fig. 1(b)]. More complex orders, such as noncollinear spirals [Fig. 1(d)] and various noncoplanar orders [e.g., Fig. 1(e)] are less common, typically arising from the interplay of magnetic exchange interactions, spin-orbit (SO) coupling, frustrated lattice structure, and magnetic field.
Dispersion
Dispersion interaction
DFT Methods for van der Waals Interactions
Non-Local Correlation (NLC) Functionals
Empirical Dispersion Corrections: DFT-D
DFT의 주요한 개발이 이루어지고 있던 2000년대 중반에 semi-local density functional (GGA)가 dispersion을 정확히 기술하지 못한다는 것이 알려졌고, 이는 최근에야 Non-local correlation (NLC) fuctionals의 개발로 어느정도 해결된 문제이다. 그럼에도 -C6/R6의 형태를 가진 empirical potential 을 도입하여 아주 빠르고 간단하게 이를 기술할 수 있다. NLC functional을 사용하지 않는 이러한 접근방식을 dispersion-corrected DFT (DFT-D)라고 한다.
DFT-D2
가장 오래된 방법은 Stefan Grimme이 개발한 DFT-D2로 다음과 같은 pairwise atomic term을 가지고 있다.
HF
Back to Top ↑Ab-initio
ORCA
Parallelization
Call ORCA by a full path (This is important so that ORCA can determine where all the different ORCA subprograms are)
Note that when running ORCA in parallel, ORCA should NOT be started with mpirun or srun
In general you should not ask for more than 75 % of the physical memory available (since ORCA occasionally will use more than the maxcore setting).
Organic
Chemical Reactions
Appel reaction
Alcohol (or Carboxylic acids) -> Alkyl chloride
GSL
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.
MKL
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.
BLAS
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.
CBLAS
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.
LAPACK
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.
ScaLAPACK
Library
MKL(Math Kernel Library)은 선형 대수 및 수치 계산에 특화되어있는 상용 소프트웨어로, BLAS, LAPACK, FFT, 벡터 수학 등의 고성능 함수를 제공한다. Intel에서 라이선스를 구입해야 하지만, 무료로 사용할 수 있는 비상업용 라이선스도 있긴 하다. MKL은 다중 스레드를 지원하며, Intel 프로세서에서 최적화되어 있어 높은 성능을 제공한다.