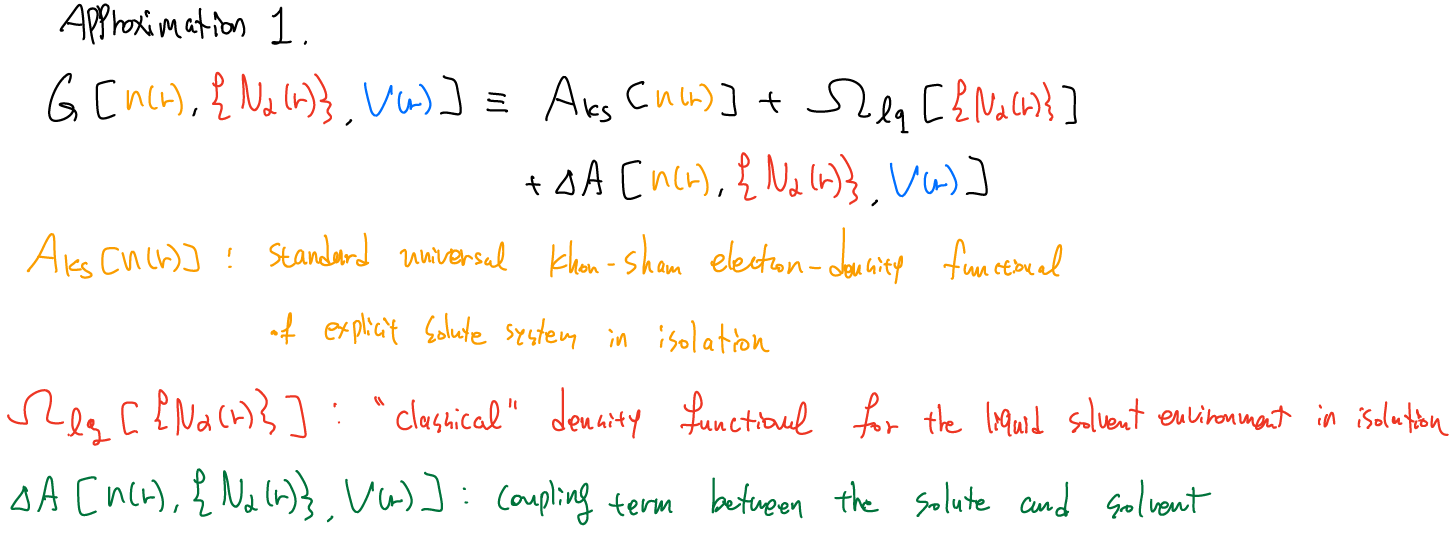실제 전기화학적 시스템에서 이온농도가 0.1 M이면 ionic screening은 30 Å 정도. 이를 explicit solvent로 구현하려면 cost가 너무 크다. 또한 phase space를 잘 sampling 하기 위해서는 굉장히 긴 시뮬레이션을 필요로 한다. 무엇보다, 실제 reaction은 Potential of zero charge (PZC)가 아닌 환경에서 일어나는데, periodic supercell calculation에서 charge를 넣고 빼려면 이를 보상해 줄 uniform charged background를 넣게 되는데, 이것은 liquid region과 solid region 모두에 적용되므로 이러한 distribution은 실제 전기화학적 환경을 정확하게 기술하지는 않는다.
다른 방법으로는 posteriori continuum model로서 물분자의 dieletric reponse와 이온의 Debye screening effect를 모두 고려하고, electrostatic potential은 Poisson-Boltzmann (PB) model을 이용하는 방법이다. Exlicit하게 몇 layer의 물 분자와 이온을 넣어 줌으로써 이 방법의 신뢰성을 더욱 높일 수 있다. 하지만 PB 모델도 정확한 theory를 바탕으로 하지는 않는다. 즉, non-locality and non-linearity of dieletric response of water 그리고 surface tension associated with formation of the liquid-solid interface를 고려하지 않는다. 즉, (modified) PB 모델은 주로 linear local dielectric response를 이용한다. 하지만 liquid-solid interface에서는 non-linear dielectric saturation effect가 존재한다. 예를들어 3 Å double layer 두께정도면 0.1 V drop이 일어나는데, (즉 field가 300 MV/m 정도) 이것은 bulk water의 dieletric constant의 1/3정도에 해당한다.
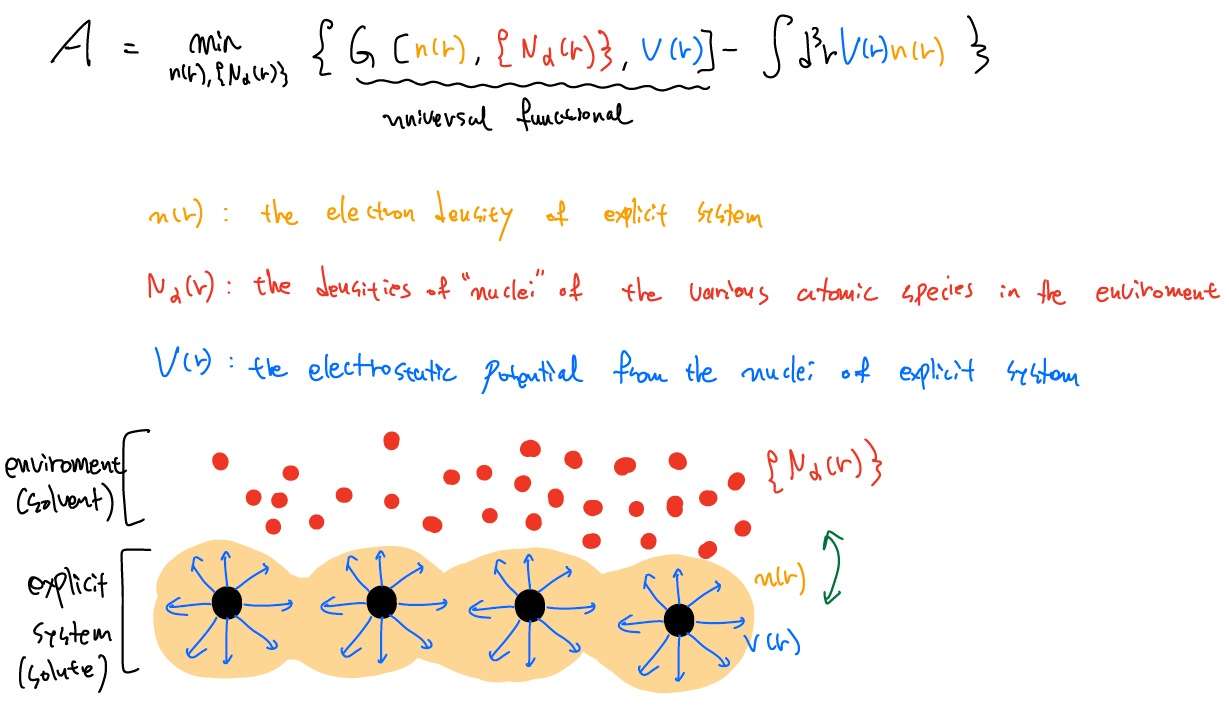
Solvent를 environment, explicit system을 solute라고 부르기로 하자. 정확한 Free energy를 구하려면, solvent 원자도 explicit하게 포함해야하고, 이들 위치의 thermodynamic averge도 구해야 하는데 최근에 joint density-functional theory (JDFT) framework에서 이것이 가능함을 매우 rigorous 하게 증명되었다. 구체적으로, liquid enviroment의 thermodynamic equilibrium을 이루는 위치가 고정된 원자의 양자역학적 시스템의 free energy A는 다음과 같이 variational principle로 구할 수 있다.
여기서 G[n(r)] 은 universal function임을 알 수 있는데, 왜냐하면, 이것은 nature of environment에 의존하고 또한 이것이 explicit system과 electron density에 의존하기 때문이다. 이 functional G를 다음과 같이 알려진 portion과 coupling term으로 나눌 수 있다고 가정하자.
- AKS[n(r)]은 잘 알려진 LDA나 GGA를 이용하여 구할 수 있다.
- 물과 같은 liquid solvent의 functional Ωlq[{Nα}]은 최근 몇년에서야 큰 developement가 이루어 지고 있다. 예를들어, 최근 연구에서 numerically efficient functional for liquid water를 이용하여 liquid와 solute의 상호작용을 결정짓는 중요한 factor들을 reproduce할 수 있었다. 예를 들어, linear and nonlinear non-local dielectric response, experimental site-site correlation functions, surface tension, bulk modulus of the liquid and the variation of this modulus with pressure, the density of liquid and the vapor phase, liquid-vapr coexistence. 이러한 functional을 이용한 framework은 linear local dielectric reponse만 기술하는 modified Poisson-Boltzmann 접근법보다 더 신뢰성 있는 방법이다. 이처럼 {Nα}의 ionic distribution을 포함시켜 이에 의한 Ωlq[{Nα}]로의 영향과 framework내에 전반적인 ionic screening을 유도하는 것이 보다 natural 하다.
- Coupling term인 ΔA의 approximate form을 개발하는 것은 open area of research로 남겨져 있다. 그 동안 여러 simplified 된 방법들이 개발 되었지만, 대표적으로 solvent molecule과 solute electron의 coupling이 작다는 사실에 기반한 the lowest-order coupling, 즉 molecular psudopotential approach가 있다. (김광수 교수님) 이 방법은 물분자들의 nuclei와 electrons의 external system (solute)로의 영향을 물분자 핵의 location {Ri}에 의존하는 “molecular pseudopotential” VRi(r)로 바꾸는 방법이다.
\[\begin{aligned} G\left[n(r),\left\{N_{\alpha}(r)\right\}, V(r)\right] \equiv & A_{K S}[n(r)]+\Omega_{l q}\left[\left\{N_{\alpha}(r)\right\}\right] \\ &+\Delta A\left[n(r),\left\{N_{\alpha}(r)\right\}, V(r)\right], \end{aligned}\]